As construction professionals and regulators push for sustainable solutions, the Expanded Shale, Clay,
and Slate Institute (ESCSI) is championing ESCS aggregates as a critical material in meeting the
industry’s
growing environmental demands.

With applications expanding in concrete durability, stormwater management, and geotechnical
stability, ESCSI’s Dr. Fariborz Tehrani emphasizes that lightweight aggregates are more than
just an
alternative—they’re a driving force for sustainable infrastructure.
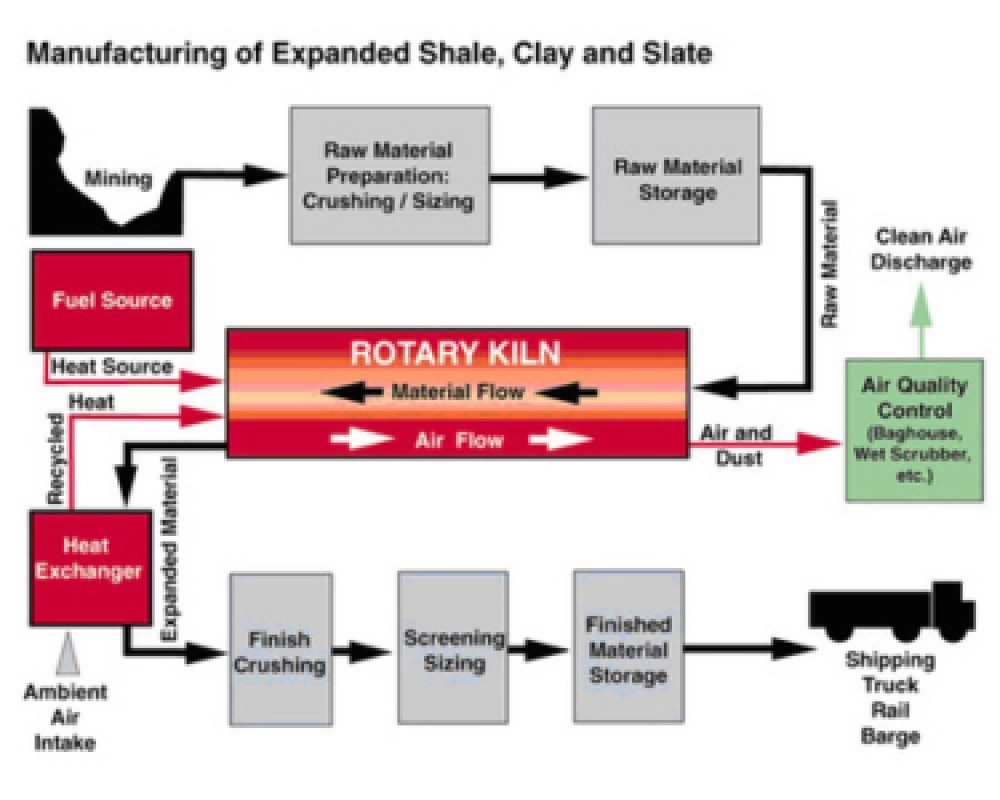
Expanded shale, clay, and slate (ESCS) aggregates are lightweight materials that provide
substantial
sustainability benefits across a range of construction and environmental applications. Created
by
heating raw materials in a rotary kiln, the unique production process causes ESCS to expand and
develop a porous structure, resulting in lightweight, durable, and highly versatile aggregates.
Enhancing Concrete Durability through Internal Curing
One of the primary sustainability advantages of ESCS is its application in concrete, where it improves
both performance and longevity. According to Dr. Fariborz Tehrani, Director of ESCSI,
“When incorporated into concrete mixtures, ESCS can enhance the material’s performance and
longevity. The porous nature of these aggregates allows them to absorb and release water, which is
particularly beneficial for internal curing.”
This process helps maintain moisture within concrete, reducing early-age
cracking and increasing structural durability.
Supporting Low-Impact Development with Stormwater Management
ESCS also contributes to sustainable urban planning through its role in
stormwater management. “These aggregates can be used in low-impact development (LID) techniques, such as
permeable surfaces and green roofs,” says Dr. Tehrani. “Their high porosity allows for efficient water
infiltration and retention, helping to mitigate urban runoff and reduce the burden on stormwater
systems.” This ability to manage urban runoff not only helps prevent flooding but also improves water
quality by filtering pollutants and supporting groundwater recharge.
Geotechnical Stability for Resilient Infrastructure
In geotechnical applications, the lightweight nature and high internal friction
of ESCS make it an excellent choice for soil stabilization and embankment construction.
“By using ESCS in these applications, engineers can reduce the overall weight of structures,
which is particularly beneficial in areas with poor soil conditions or seismic activity,” Dr. Tehrani
explains.
This reduction in weight contributes to safer and more resilient
infrastructure, enhancing the sustainability of construction projects.
Eco-Friendly Production and Local Sourcing
The production process of ESCS is efficient and environmentally friendly. “The
raw materials used for ESCS are abundant and often sourced locally, reducing transportation-related
emissions and supporting local economies,” notes Dr. Tehrani. Additionally, the expansive nature of ESCS
production means significantly less raw material is needed—up to one-third to one-half less than
conventional aggregates—to achieve the same volume in final products.
Driving Sustainable Construction Forward
With diverse applications and an eco-friendly production process, ESCS
aggregates are well-suited to sustainable construction. “Expanded shale, clay, and slate offer numerous
sustainability benefits, from enhancing concrete durability and stormwater management to improving
geotechnical stability and reducing environmental impact,” Dr. Tehrani concludes.